IFT Notes for Level I CFA® Program
LM02 Financial Reporting Standards
Part 2
5. The International Financial Reporting Standards Framework
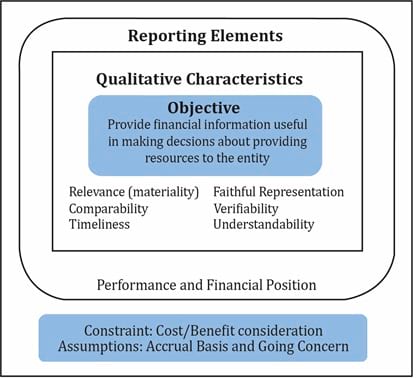
The IFRS has prepared a framework for the preparation and presentation of financial reports. The framework is shown in the diagram below.
Objective of financial statements
At the center of the framework is the objective of financial statements. As per the IFRS framework, the objective of financial statements is ‘to provide financial information about the reporting entity that is useful to existing and potential investors, lenders, and other creditors in making decisions about providing resources to the entity.’
The IASB Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting is designed to:
- “assist standard setters in developing and reviewing standards;
- assist preparers of financial statements in applying standards and in dealing with issues not specifically covered by standard;
- assist auditors in forming an opinion on financial statements; and
- assist users in interpreting financial statement information. “
Qualitative characteristics
Surrounding the objective are the desirable qualitative characteristics of financial statements.
The two fundamental qualitative characteristics are:
- Relevance: Financial statements should be useful, both for making forecasts as well as to evaluate past forecasts. They should be timely and sufficiently detailed and important facts should not be omitted.
- Faithful representation: Information presented should be complete, neutral, and free from errors.
The four supplementary qualitative characteristics are:
- Comparability: Financial statements should be consistent over time and across firms to facilitate comparisons.
- Verifiability: Independent observers should be able to verify that information reflects true economic reality.
- Timeliness: Information should be available in a timely manner.
- Understandability: Information should be presented in a simple manner, such that even users with basic business knowledge can understand it.
6. The Elements of Financial Statements
Surrounding the qualitative characteristics are the reporting elements used to present information.
Elements related to measurement of financial position are:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
Elements related to measurement of financial performance are:
Below the reporting elements are the constraints faced and the assumptions made while preparing financial statements.
Constraints
- Tradeoff between reliability and timeliness: If a firm tries to make statements that have no errors and are highly reliable it will need a lot of time. Similarly, if a firm tries to make statements in the least amount of time they will more errors and be less reliable.
- Cost: The benefit that the users gain from using the reports should be more than the cost of preparing the reports.
- Intangible aspects: Intangible information such as brand name and customer loyalty cannot be captured directly in financial statements.
Assumptions
- Accrual basis: Revenue should be recognized when earned and expenses should be recognized when incurred, irrespective of when the cash is actually paid.
- Going concern: Assumption that the company will continue operating for the foreseeable future.
7. General Requirements for Financial Statements (IASB)
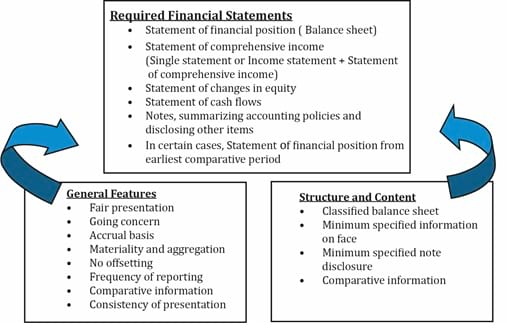
Required financial statements
The required financial statements are:
- Balance sheet.
- Income statement.
- Cash flow statement.
- Statement of changes in owners’ equity.
- Explanatory notes.
General features for preparing financial statements
The general features for preparing financial statements are:
- Fair presentation: Faithful representation of transactions.
- Going concern: Assume firm will continue to exist for the foreseeable future.
- Accrual basis: Recognize revenue when earned and expense when incurred.
- Materiality and aggregation: Important information should not be omitted. Similar information should be grouped together.
- No offsetting: Assets and liabilities, and revenue and expenses should not be offset against each other.
- Frequency of reporting: Prepare statements at least annually.
- Comparative information: Comparable information for prior periods should be included.
- Consistency: Prepare reports in the same manner for every period.
Structure and content requirements
Firms should use the classified balance sheet structure (which shows current and non-current assets and liabilities separately.) Certain minimum information must be presented in the notes and on the face of the financial statements.
8. Comparison of IFRS with Alternative Reporting Systems
A significant percentage of listed companies use either IFRS or US GAAP. An analyst must be cautious when comparing financial measures between companies reporting under IFRS and companies reporting under US GAAP. If needed, specific adjustments need to be made to achieve comparability.
US GAAP uses standards issued by FASB while IFRS uses standards issued by IASB. While the two organizations are working towards convergence, significant differences still remain.
Differences between IFRS and US GAAP:
| Basis for Comparison |
US GAAP |
IFRS |
| Developed by |
Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB). |
International Accounting Standard Board (IASB). |
| Based on |
Rules |
Principles |
| Inventory valuation |
FIFO, LIFO and Weighted Average Method. |
FIFO and Weighted Average Method. |
| Extraordinary items |
Shown below (at the bottom of the income statement). |
Not segregated in the income statement. |
| Development cost |
Treated as an expense |
Capitalized, only if certain conditions are satisfied. |
| Reversal of Inventory |
Prohibited |
Permissible, if specified conditions are met. |
Source: CFAI Curriculum 2020; https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-gaap-and-ifrs.html
9. Monitoring Developments in Financial Reporting Standards
Analysts must be aware that reporting standards are evolving rapidly. They need to monitor developments in financial reporting and assess their implications for security analysis and valuation.
A financial analyst can remain aware of developments in financial reporting standards by monitoring three sources:
- new products or transactions
- actions of standard setters and groups representing users of financial statements
- company’s disclosures regarding critical accounting policies and estimates.
Share on :

