101 Concepts for the Level I Exam
Concept 17: Price, Income and Cross-Price Elasticities of Demand
![]()
Elasticity of demand is measured as a ratio of percentage change in quantity demanded to a percentage change in other variables.
Own-price elasticity
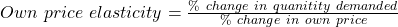
- Own-price elasticity of demand is usually always negative.
- If |own price elasticity| > 1, then demand is elastic.
- If |own price elasticity| < 1, then demand is inelastic.
- If own price elasticity = -1, then demand is unit, or unitary, elastic.
Income elasticity
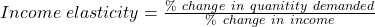
- If income elasticity > 0, then the good is a normal good.
- If income elasticity < 0, then the good is an inferior good.
Cross price elasticity
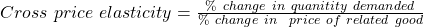
- If cross price elasticity > 0, then the related good is a substitute.
- If cross price elasticity < 0, then the related good is a complement.
A demand function for chairs is as follows:
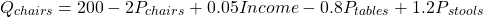
At current average prices, a chair costs $50, a table costs $100 and a stool costs $30. Average income is $5,000. Calculate the income elasticity of demand for chairs.
Solution:
Substitute current values for the independent variables (except income)
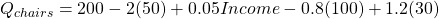
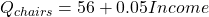
The slope of income is 0.05
For an income of $5,000; Qchairs = 306
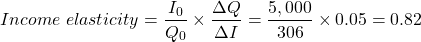
Factors impacting the own price elasticity of demand for a product include:
- Substitutes: If the number of substitutes for this product is high, then elasticity will be high.
- Portion of total budget: If the portion of total budget spent on this product is high, then elasticity will be high.
- Time horizon: If the time horizon we consider is long, then elasticity will be high. This is because consumers will have enough time to respond to changes in the price of this product.
- Discretionary (optional) versus non-discretionary (necessary): If the product is discretionary rather than non-discretionary, then the elasticity will be high.
Share on :


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()