101 Concepts for the Level I Exam
Essential Concept 17: Theories of Economic Growth
![]()
Classical Model (also called Malthusian Theory)
- Growth in real GDP per capita is temporary.
- Rise in real GDP per capita above subsistence level results in a population explosion.
- Real GDP per capita returns to subsistence level.
Neo-Classical Model
- In steady state capital per worker and output per worker grow at equal sustainable rates.
- Long-run per capita growth depends on exogenous technological progress.
- Capital deepening has no impact on growth rate or on marginal product of capital.
- There will be convergence of per capita income in developing and developed countries.
Three important relationships to remember are:
- Growth rate of output per capita =
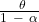
- Growth rate of output =
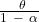 + n
+ n
-
Output per unit of capital
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com = \frac{\mathrm{Y}}{\mathrm{K}}\mathrm{=}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{s}}\right)\left[\left(\frac{\mathrm{\theta }}{\mathrm{1\ -\ }\mathrm{\alpha }}\right)\mathrm{+}\mathrm{\delta }\mathrm{+n}\right]](https://ift.world/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6cbc0c302349a823464f2d9b00d7b719_l3.png)
Endogenous Growth Theory
- Focus on explaining technological progress rather than treating as exogenous.
- It states that there is no reason why incomes of developed and developing countries should converge.
- A higher saving rate can permanently higher growth rate.
An important relationship to remember is:
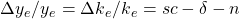
Share on :


![]()